Slit a tree at a given internal node into a clade rooted at this node and the remaining tree after dropping this clade
PCMTreeSplitAtNode.RdSlit a tree at a given internal node into a clade rooted at this node and the remaining tree after dropping this clade
PCMTreeSplitAtNode( tree, node, tableAncestors = PCMTreeTableAncestors(tree), X = NULL )
Arguments
| tree | a PCMTree object. |
|---|---|
| node | an integer or character indicating a root, internal or tip node |
| tableAncestors | an integer matrix returned by a previous call to PCMTreeTableAncestors(tree) or NULL. |
| X | an optional k x N matrix with trait value vectors for each tip in tree. |
Value
A list containing two named phylo objects:
clade The subtree (clade) starting at
node.Xclade The portion of X attributable to the tips in clade; NULL if X is NULL.
rest The tree resulting after dropping all tips in the clade.
Xrest The portion of X attributable to the tips in rest; NULL if X is NULL.
Details
In the current implementation, the edge.jump and edge.part members of the tree will be discarded and not present in the clade.
Examples
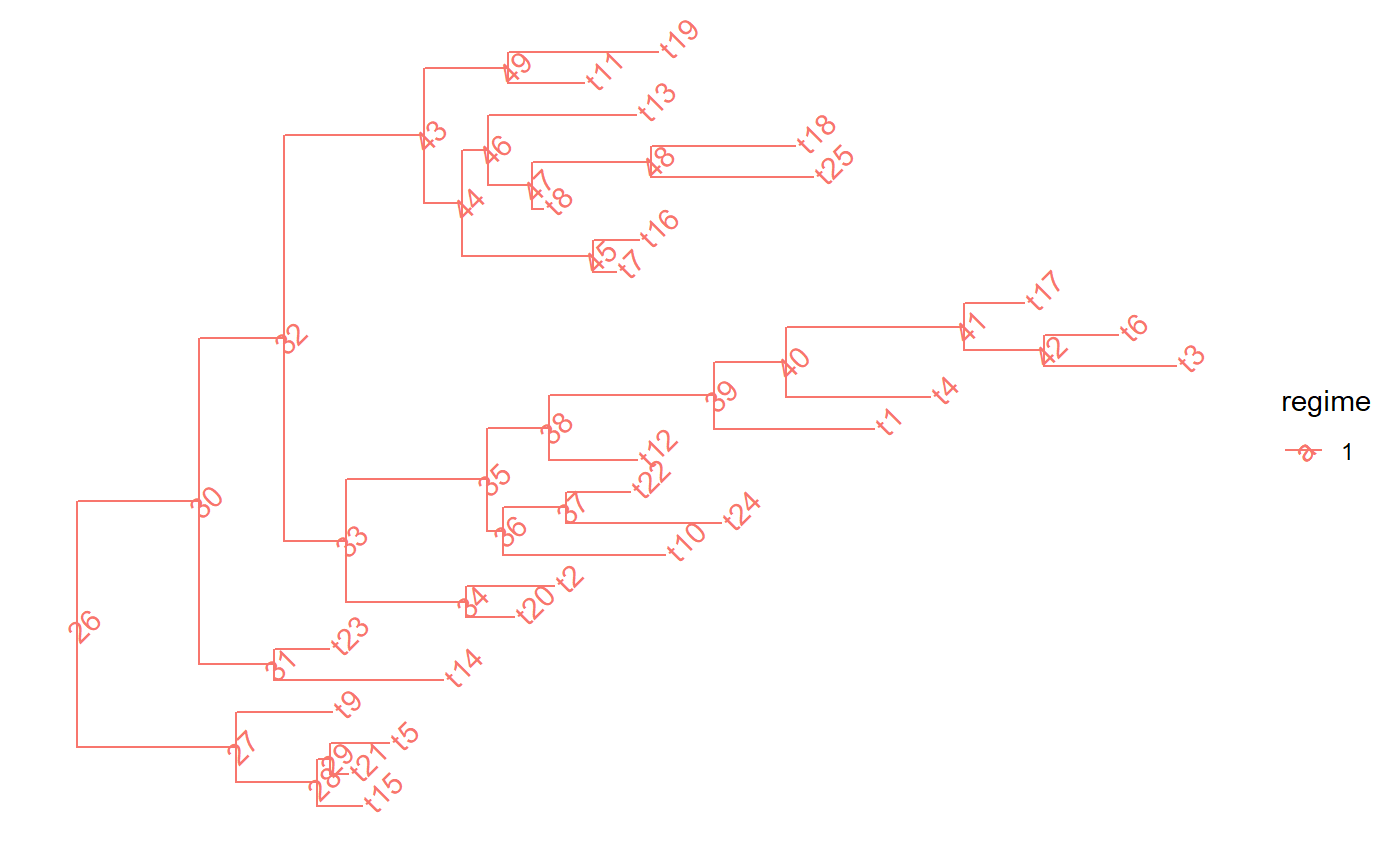
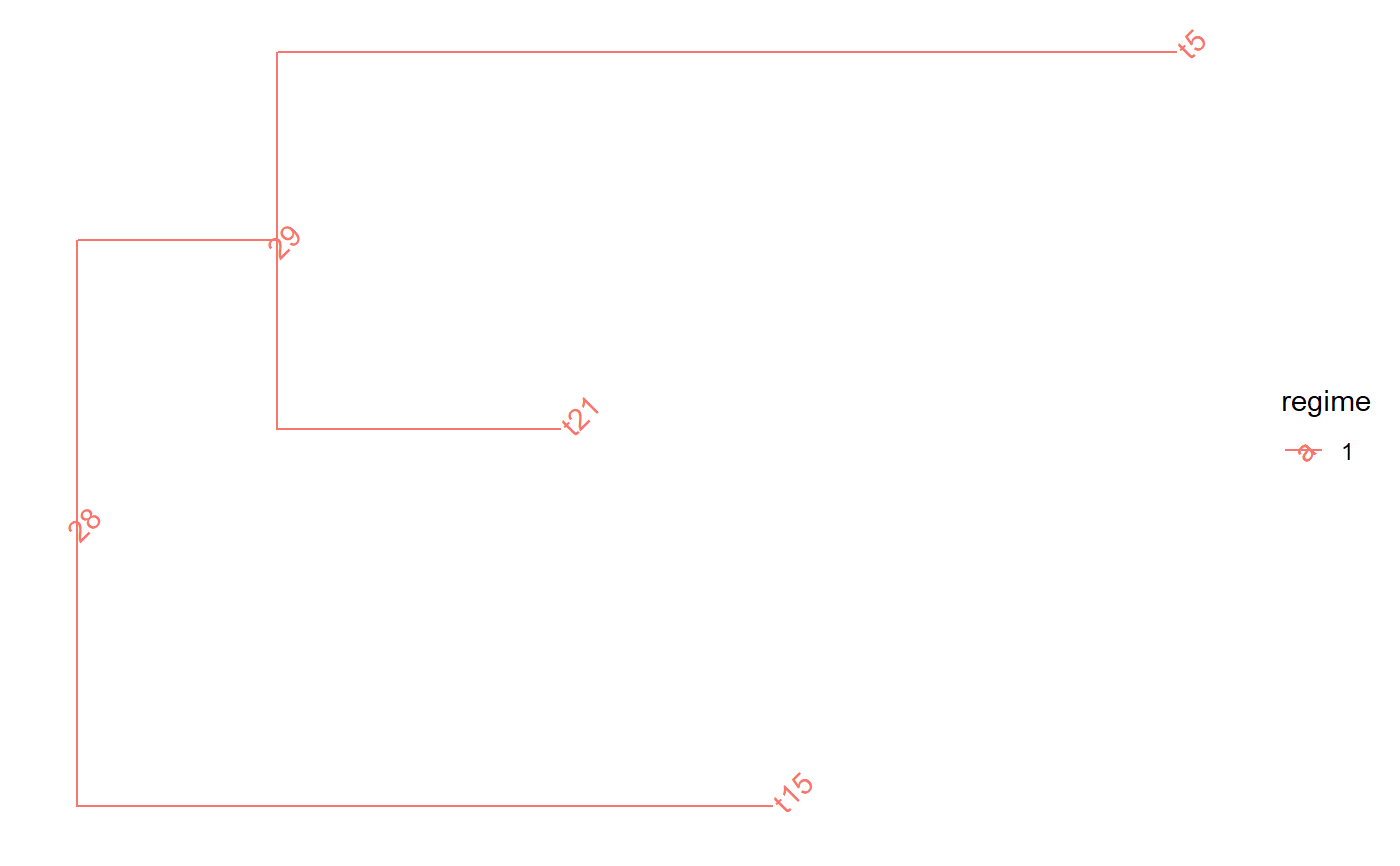
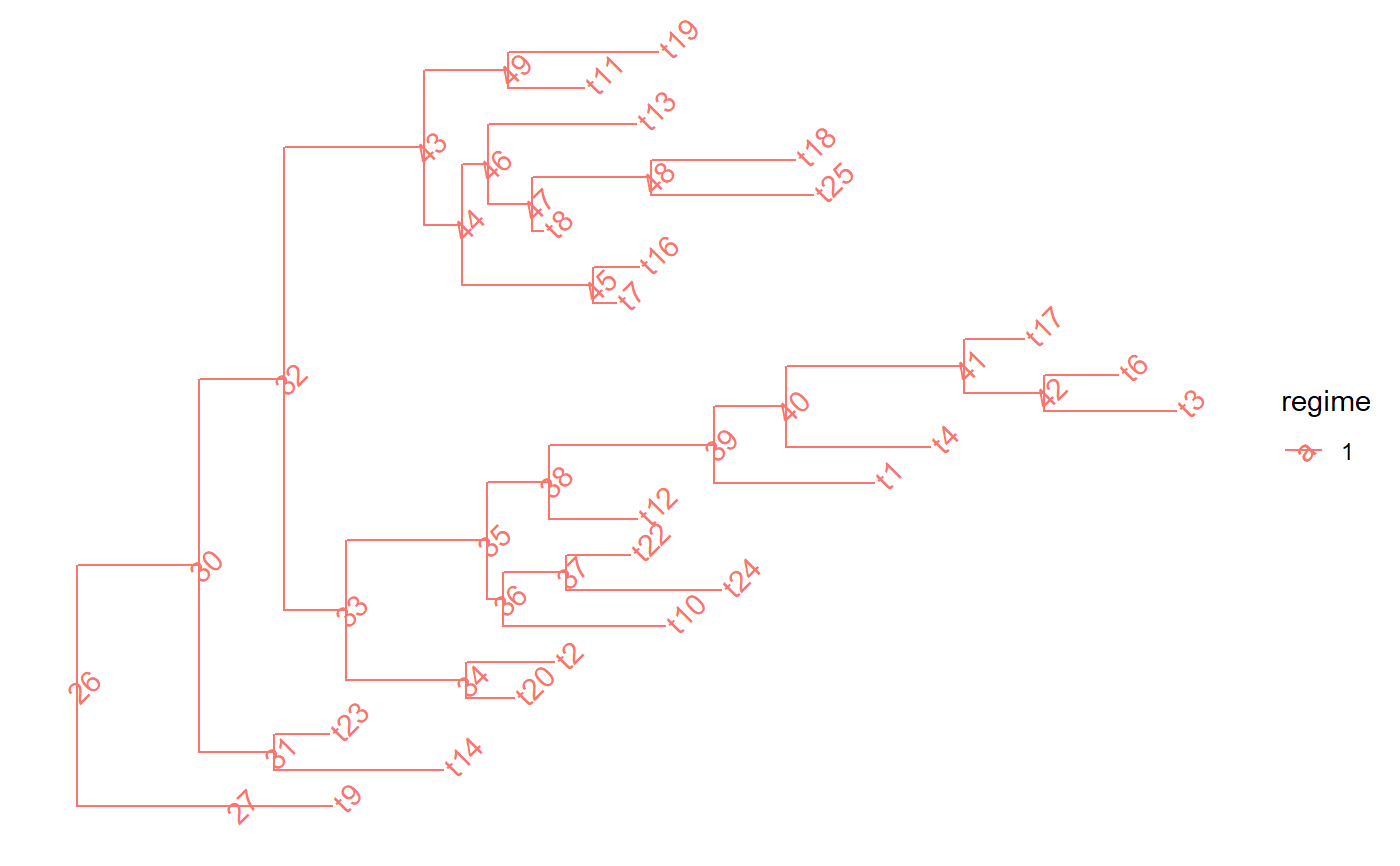
set.seed(1, kind = "Mersenne-Twister", normal.kind = "Inversion") tree <- PCMTree(ape::rtree(25)) # \donttest{ PCMTreePlot(tree) + ggtree::geom_nodelab(angle = 45) + ggtree::geom_tiplab(angle = 45)# } spl <- PCMTreeSplitAtNode(tree, 28) # \donttest{ PCMTreePlot(PCMTree(spl$clade)) + ggtree::geom_nodelab(angle = 45) + ggtree::geom_tiplab(angle = 45)# } # \donttest{ PCMTreePlot(PCMTree(spl$rest)) + ggtree::geom_nodelab(angle = 45) + ggtree::geom_tiplab(angle = 45)# }