Inferring an MGPM with Unknown Shifts
Venelin Mitov
2021-06-05
Source:vignettes/ResultsBootstrap/MGPM_A_F_BC2_RR_BSID_1/vignettes/pcmfitmixed.Rmd
pcmfitmixed.RmdNote: The writing of this vignette is currently in progress. If needed, please, contact the author for assistance. Thanks for your understanding.
The main R-script
Setting up a parallel cluster
Using MPI
# creating the cluster for this PCMFit run:
if(!exists("cluster") || is.null(cluster)) {
if(require(doMPI)) {
# using MPI cluster as distributed node cluster (possibly running on a
# cluster of multiple nodes)
# Get the number of cores. Assume this is run in a batch job.
p = strtoi(Sys.getenv('LSB_DJOB_NUMPROC'))
cluster <- startMPIcluster(count = p-1, verbose = TRUE)
doMPI::registerDoMPI(cluster)
} else {
warning("Could not create an MPI cluster")
}
}Using a personal computer without mpi installation
if(!exists("cluster") || is.null(cluster)) {
if(require(parallel)) {
# possibly running on personal computer without mpi installation
cluster <- parallel::makeCluster(
parallel::detectCores(logical = TRUE),
outfile = paste0("log_", prefixFiles, ".txt"))
doParallel::registerDoParallel(cluster)
} else {
warning("Could not create a parallel cluster")
}
}Generating PCMModels on the worker nodes
# This function is going to be executed on each worker node.
generatePCMModelsFunction <- function() {
# make results reproducible
set.seed(4, kind = "Mersenne-Twister", normal.kind = "Inversion")
PCMGenerateModelTypes()
# An example DefineParameterLimits.R file can be found in
# vignettes/DefineParameterLimits.R of the PCMFit package source-code.
# Note that the path here is relative to the working directory of
# the worker node R-process.
source('DefineParameterLimits.R', local=FALSE)
}Tree and trait data
tree <- PCMTree(PCMFitDemoObjects$dtSimulated$tree[[1]])
X <- PCMFitDemoObjects$dtSimulated$X[[1]][, seq_len(PCMTreeNumTips(tree))]Running the MGPM Inference
currentResultFile <- paste0("Current_", prefixFiles, ".RData")
if(file.exists(currentResultFile)) {
load(currentResultFile)
tableFitsPrev <- listResults$tableFits
} else {
tableFitsPrev <- NULL
}
fitMGPM_A_F_BC2_RR <- PCMFitMixed(
X = X, tree = tree, metaIFun = PCMInfoCpp,
generatePCMModelsFun = generatePCMModelsFunction,
maxNumRoundRobins = 2, maxNumPartitionsInRoundRobins = 2,
tableFitsPrev = tableFitsPrev,
prefixFiles = prefixFiles,
doParallel = TRUE)Retrieving and analyzing the best scoring model fit
bestFit <- RetrieveBestFitScore(fitMGPM_A_F_BC2_RR)
modelTrue <- PCMFitDemoObjects$dtSimulated$model[[1]]
# We specify the tree and trait values for the true model in order to easily
# calculate parameter count likelihood and AIC for it:
attr(modelTrue, "tree") <- PCMFitDemoObjects$dtSimulated$treeWithRegimes[[1]]
attr(modelTrue, "X") <- X
attr(modelTrue, "SE") <- X * 0.0
listModels <- list(
RetrieveBestModel(PCMFitDemoObjects$fitBM),
RetrieveBestModel(PCMFitDemoObjects$fitOU),
RetrieveBestModel(PCMFitDemoObjects$fitMGPMTrueTypeMapping),
RetrieveBestModel(PCMFitDemoObjects$fitMGPMTrueTypeMappingCheat),
modelTrue,
bestFit$inferredModel)
dtSummary <- data.table(
model = c(
"Global BM",
"Global OU",
"True MGPM, known shifts, unknown parameters",
"True MGPM, known shifts, starting from known true parameters (cheating)",
"True MGPM, fixed true shifts and true parameters",
"Inferred MGPM, unknown shifts and parameters"),
p = sapply(listModels, PCMParamCount),
logLik = sapply(listModels, logLik),
AIC = sapply(listModels, AIC))
knitr::kable(dtSummary)| model | p | logLik | AIC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global BM | 5 | -221.68133 | 455.3627 |
| Global OU | 11 | -204.60164 | 433.2033 |
| True MGPM, known shifts, unknown parameters | 18 | -93.65584 | 233.3117 |
| True MGPM, known shifts, starting from known true parameters (cheating) | 18 | -93.50648 | 233.0130 |
| True MGPM, fixed true shifts and true parameters | 18 | -102.63502 | 251.2700 |
| Inferred MGPM, unknown shifts and parameters | 17 | -95.07409 | 234.1482 |
#> ggtree v2.0.4 For help: https://yulab-smu.github.io/treedata-book/
#>
#> If you use ggtree in published research, please cite the most appropriate paper(s):
#>
#> [36m-[39m Guangchuang Yu, Tommy Tsan-Yuk Lam, Huachen Zhu, Yi Guan. Two methods for mapping and visualizing associated data on phylogeny using ggtree. Molecular Biology and Evolution 2018, 35(12):3041-3043. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msy194
#> [36m-[39m Guangchuang Yu, David Smith, Huachen Zhu, Yi Guan, Tommy Tsan-Yuk Lam. ggtree: an R package for visualization and annotation of phylogenetic trees with their covariates and other associated data. Methods in Ecology and Evolution 2017, 8(1):28-36, doi:10.1111/2041-210X.12628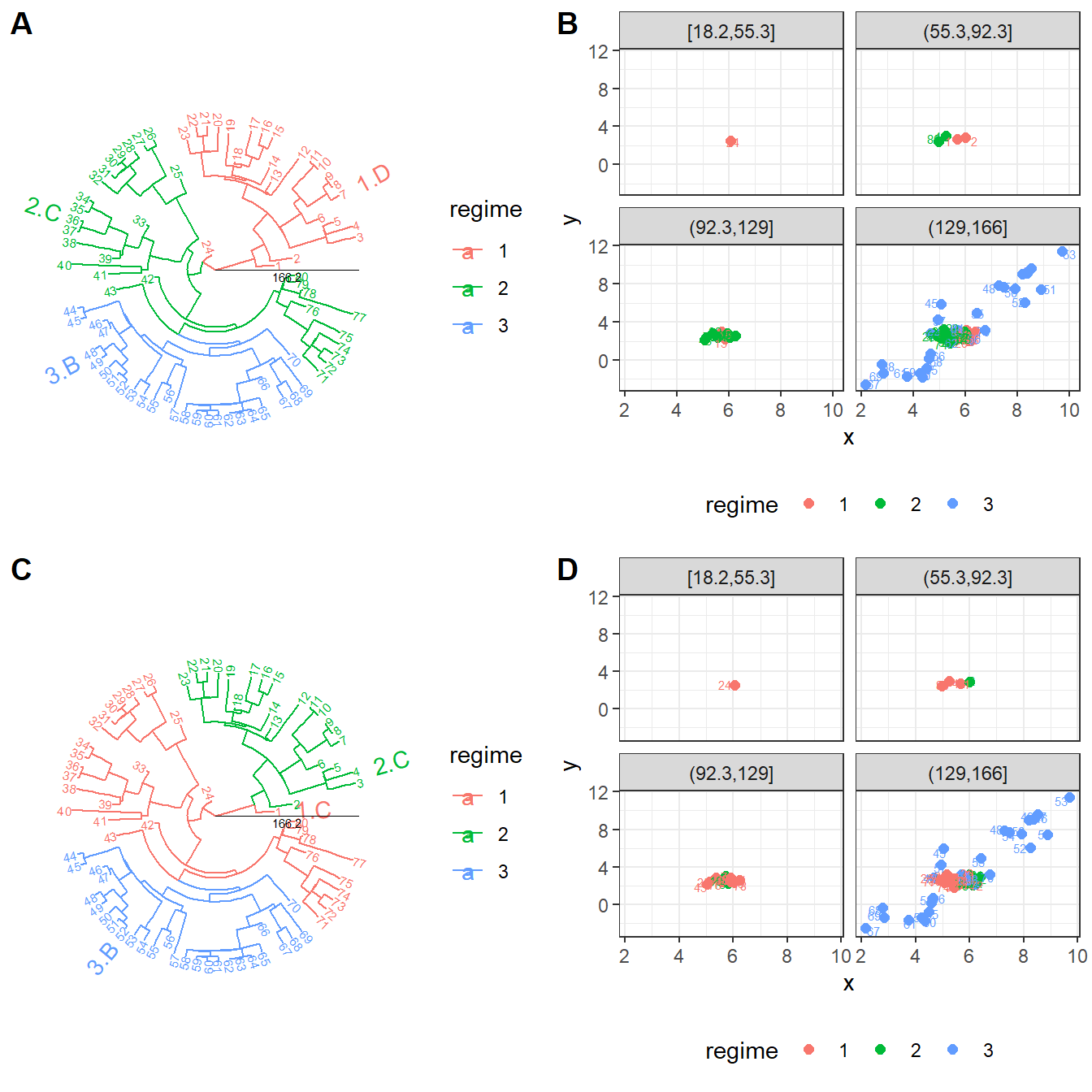
Example phylogenetic comparative data. A: a tree of 80 tips partitioned in three evolutionary regimes. Each evolutionary regime is denoted by #.T, where # is the regime identifier and T is the evolutionary model type associated with this regime (a model type among A, …, F). B: bivariate trait values at the tips of the tree. C and D: Analogical to A and B according to the MGPM found using the AIC score as a criterion.